VIDEO
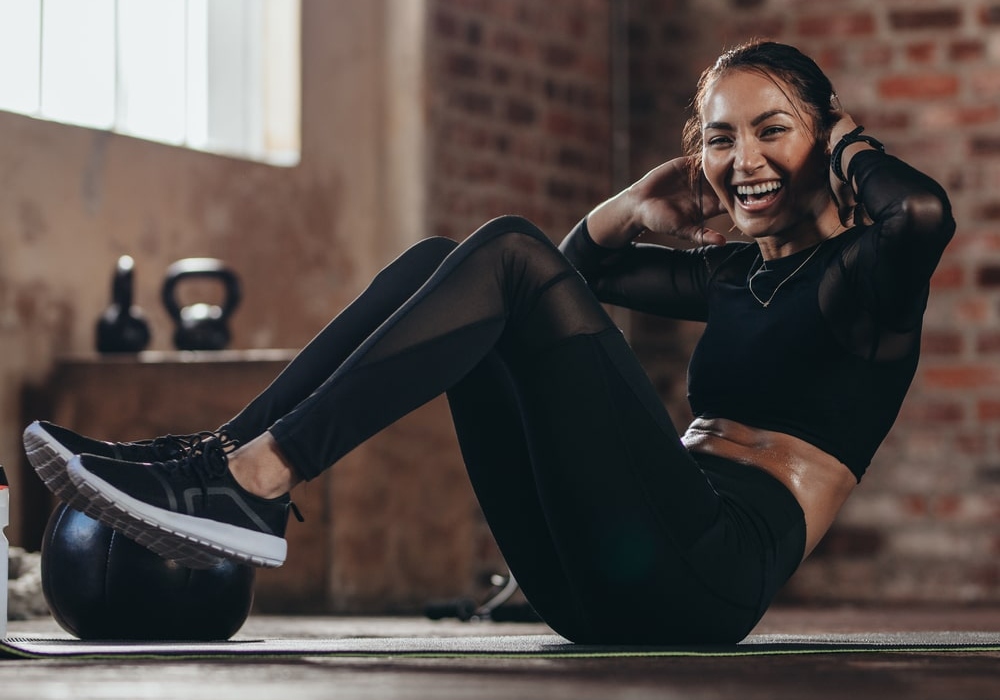
Kettlebell Turkish Getup
- Core
- Back
- Abs
- Biceps
- Triceps
- Gluteus
- Quads
- Hamstrings
Level:Advanced
Trainer:Nick Taylor
Equipment:Kettlebell
Kettlebell Turkish Getup
- Core
- Back
- Abs
- Biceps
- Triceps
- Gluteus
- Quads
- Hamstrings
Level:Advanced
Trainer:Nick Taylor
Equipment:Kettlebell
Lay flat on your back and grab a kettlebell in one hand. You need to have your second arm and the same leg extended. The foot on the side of the kettlebell should rest firmly on the floor. Leaning on your elbow, push your torso upward. From this position get up on your hand. Swinging the extended foot back get up into a lunge. Finally stand up. repeat all the action in reverse, so that in the end you are in the starting position.
save to ...
RECOMMENDED FOR YOU
ARTICLES
The most important muscles in the upper back are the lats and trapezius.
Lats (Latissimus dorsi). Shaping muscles of the back, giving the figure a tapered appearance. Visually widen the shoulders and make the waist appear narrower. They are located on both sides of the spine, and their shape resembles a wing.
Trapezius muscles. These are the muscles that need to be trained if you want to correct the slouch. Responsible for the movement of the scapula. They have a triangular shape; in the upper part, they are attached to the back of the head, in the lower part - to the spine.
Be careful, ‘cos back exercises are some of the most traumatic. In the early stages, use light weights to strengthen the ligaments and muscles to protect the spine. After mastering the technique, gradually and very gently increase the weight.
The upper and horizontal rows are the exercises closest to the anatomical movement of the joints.
Training
Wide grip pull-ups. Pulling up is one of the main exercises for back muscle growth, performed with body weight. First, learn how to pull up correctly, and only then move on to training with dumbbells or a barbell. It is important that when performing the exercise, you should feel the work of the back muscles, not the biceps. Grab the horizontal bar with an upper grip, arms slightly wider than shoulder-width. When pulling up, try to pull the body up not with your hands, but with your back. Pause for a second at the top point, smoothly return to the starting position.
Upper block thrust. The exercise imitates pulling up, go to it only when you learn to pull up, and you can do it at least 8-10 times per set. Important: pulling the bar towards your chest, not your head - this will reduce the dangerous load on your shoulders, a signal of improper performance - to feel the work of the hands. If you can't feel your back, use less weight. increase the width of the grip every time - this has a positive effect on the 'growth' of the back.
Seated pulldown. A basic exercise that includes a large muscle mass, especially the pectorals and lats. One of the best for giving the back a visual width. With a straight bar (see photo), the trapezius muscles are also included in the work.
Make sure that the cable is parallel to the floor during the exercise, the torso does not change the slope, and the back is straight.
Shrugs. Almost the only exercise for isolated work on the trapezius muscles. There are many variations - with dumbbells, with a barbell, standing, sitting or lying down. The photo shows an option sitting on a bench with dumbbells.
When lifting the dumbbells up, you can lower your chin slightly, which will increase the load on the muscles. It is important not to rotate your shoulders or relax them at the bottom of the exercise - this is very dangerous for the joints.
One-arm dumbbell row. Place your knee and hand on the bench. Take the dumbbell with your other hand, pull it as close to your chest as possible, then slowly lower it down. Make sure that your back is parallel to the floor during the exercise, do not round it; do not drop your non-working shoulder.
Important:
As soon as the elbow is at shoulder level, connect the shoulder to the movement - pull it up with the elbow. This will maximize the contraction of your mid-back and upper lats.
If you are having trouble getting your elbow higher than your shoulder, use a lighter dumbbell.
Read more
The oblique abdominal muscles are several groups of abdominal muscles on the sides of the core. The external oblique muscle lies on top and the internal oblique muscle - below it. Functional exercises for training them are bending, turning to the sides, and other rotating movements.
However, in order to work your obliques properly, you must remember that most exercises for the oblique muscles involve the other abdominal muscles, the inner transverse muscles, in particular. That's why you need to be able to consciously engage certain areas of the abs during the workout.
The oblique muscles represent the lateral part of the abdominal area. They act as the main rotators of the body. They are represented by two separate muscles, depending on depth and layer:
The outer oblique abdominal muscle forms the superficial layer. It is usually the target of training. It anatomically begins from ribs 5-12.
The internal muscle originates from the lumbosacral fascia, iliac crest, and inguinal ligament. It is attached to the area of the white line, cartilages of ribs 9-12, and pubic crest.
The main task of the oblique abs is to rotate the torso. Although, in addition to the main one, the muscle performs a number of functions:
Tilting of the torso.
Flexion.
Lowering the ribs.
The tension of the anterior abdominal chest wall.
Bilateral contraction.
In general, in order to work your abs properly, it is necessary to follow simple recommendations:
Eat lightly 2-2.5 hours before the exercise. If you train with an empty stomach, you will not work out to your full potential, which means that the workout will be ineffective. An overfilled stomach can also leave negative consequences, such as nausea and severe dizziness.
Warm up your muscles by doing light exercises. Jump, run on the spot or on a machine, do simple tricks like turns, twists, and turns.
Do not overdo it! You don't need to exhaust yourself every day. Try 2-4 times a week - that will be enough for a nice and shapely belly.
Each exercise should stretch your muscles. You should feel how they are tensed. If this is not there, then you are doing something wrong.
Do not eat immediately after the workout. If you feel very hungry, snack on an apple or drink a glass of water. Do not eat after one hour at the earliest.
Read more
The trapezius muscle is a crucial straight broad muscle that is located in a superficial position, in the back part of the neck and the upper back. The trapezius muscle has the shape of a triangle, the base facing the spinal column, and the top - to the acromion of the scapula. These kinds of muscles on both sides of the back together are trapezoidal.
There are three parts of it:
Upper part: Once the spine is fixed and raises the scapula. With a fixed shoulder blade, it straightens the head and neck.
Middle part: When the spine is fixed and the head brings the scapula to the spine. With the contraction of all parts of the muscles, the adduction of the shoulder blades also occurs.
Low part: It downs the shoulder girdle when the spine and head are fixed.
The upper trapezius muscles are trained by raising and lowering the shoulders with weights in the hands (performing shrugs). The lower part is trained by bringing the shoulder blades of the back under load.
Training.
Band Seated Row. Sitting on the floor with your legs extended loop an elastic band around your soles and hold one end in your right hand. Squeezing your shoulder blades and making a twist to the right with your torso, pull the band toward your waist. Then repeat the action to the other side.
Planche. It is an advanced gymnastic exercise. You should have a high level of fitness preparation and strong hands. It is the skill in which your body should be parallel to the ground supported by hands and arms with your legs raised.
S-Leg Pushup. Put your hands and toes on the mat. Keep your arms straight, but don't lock your elbows. Align your feet making the straight line with your arms and core. Inhaling, bend your elbows and lower your chest to the mat slowly. Straighten your arms to lift your core up, exhaling, at the same time lifting one leg off the ground.
P-up Variation. Put your hands and toes on the mat. Keep your arms straight, but don't lock your elbows. Align your feet making the straight line with your arms and core. Inhaling, bend your elbows and lower your chest to the bench slowly. Straighten your arms to lift your core up, exhaling.
Read more
The core is a series of muscles that start under the pectoral and extend to the pelvis. It also includes several groups in the back and other groups throughout the torso. A 'strong back' means a good physique and a healthy body. If you want to learn how to do this, learn to exercise at home or at the gym. Once you have achieved this strength, you can also learn to maintain it.
The midsection is the area of the body often referred to as the core and it involves everything in that area including the front, back and sides. It includes:
lower back.
the traverse abdominis (TVA);
erector spinae;
obliques;
If they are week it could cause lower back and waist pain. However, taking care of them can keep your posture healthy and make you stronger in other exercises like running and walking.
Training. One of the best core exercises is a plank. It provides minimal movement but maximal effort, demanding you to support your body on your hands and toes during holding your body in a straight line from your shoulders to your ankles. Also, you can rest on your knees If you need it or make it more difficult by extending your arms so you’re supported by your hands.
Bridge. Lie down on the floor. Put your arms straight down on the floor near your hips. Bend your knees. Lift your hips up and down.
Superman. Do a little push-up. Lie with your face down and stretch and arms forward and your legs backward.
V-Jumps. Sit on a bench or chair, lift your legs, tilt the core slightly forward so that your body forms a 45-degree angle. From this position jump up extending your hands above your head.
Pushup Variation. Put your hands and toes on the mat. Keep your arms straight, but don't lock your elbows. Align your feet making the straight line with your arms. Inhaling, lower your chest to the ground slowly. Straighten your arms to lift your core up, exhaling.
Inchworm Variation. Put your hands on the ground and your feet - on the elevated surface (a bench). Start walking your hands out, as far as you can keeping your legs straight throughout the movement. Make a pause. Walk your hands back up to the starting position.
Reverse Crunches Variation. Bend your legs at the knees and brace your abs to slowly raise your legs so that your knees are directly over your hips. Brace abs and hold the neutral spine position with a slight neutral curve in the lower back. Exhale as you contract the abs Your head should be kept straight and relaxed on the mat. Inhale and slowly return to the starting position.
Read more
The muscle on the back of your shoulder is called the triceps. Triceps originate from the scapula and humerus and attach to the ulna using the triceps tendon. The triceps muscle does the function of extension in the elbow and acts as an auxiliary in the implementation of other movements in the shoulder. During triceps contraction, the vector of movement is transmitted using the tendon.
The mass fraction of the triceps is approximately 2/3 of the muscles of the shoulder, so its size plays a critical role in the formation of beautiful arms. By focusing on the biceps, and forgetting about the triceps muscle, athletes contribute to getting inharmoniously developed arms.
You shouldn't train your triceps more often than 1-2 times a week. Do not forget that many exercises for the pectoral muscles load the triceps, so make up the training program so that the triceps and pectoral muscles are trained on different and distant days, thus some periodization of the load is achieved.
But in some cases, the triceps can be trained on the same day as the pectorals, since all basic chest exercises involve the triceps and vice versa. This means that if you swing your chest, then the triceps already swing by themselves. To increase efficiency, do triceps workouts of different intensities: light-medium-hard, and so on. Rest for at least 1 week after a hard workout.
In classic splits, the triceps are usually the most overloaded muscle, due to the very specifics of training in split programs. To increase the volume of the triceps muscle, do 8-15 repetitions. The total number of triceps sets (the sum of the sets of all triceps exercises) is 3-6.
The basic exercises for pumping triceps are reverse push-ups on the bench and narrow grip barbell press. In addition, an important exercise is a pull of the upper block with a rope - one of the few that uses the lateral head in the work. Since the mechanics of movements are in many ways similar, it is recommended not to combine the presented exercises, but to alternate.
Training.
Reverse push-ups from the bench. Starting position - heels touch the floor, hands on the bench behind your back. Slowly lower your torso down, linger at the bottom point, then with an explosive force push your body weight up over the bench. The elbows are directed backward. To complicate things, use an extra load by putting the weight on your hips.
Bench press with a narrow grip. It’s the exercise to work out the medial head of the triceps. Lie on a bench (keeping your feet firmly on the floor), grab a barbell or dumbbell with a narrow grip, then lift the weight up. During execution, the elbows should be pressed as close to the body as possible.
Bent over triceps extension. It’s for pumping the long and lateral heads of the triceps. When pulling the arm back, make sure that the elbow does not change position (that is, do not swing the arm back and forth or left and right). Also, watch out for the arch of the back - to do this, keep the abs slightly tense.
Top pulldown with rope. A key exercise for pumping the lateral head of the triceps. The movement should be in the lower plane - that is, do not raise your arms higher than chest level. When doing it, make sure that the elbows do not change position, and the body does not swing.
Remember that when building the triceps, you need to correctly feel the amplitude of the exercises - achieving maximum involvement of the muscles without dangerous impact on the shoulder joint. For this, it is better to use an average working weight.
Furthermore, watch your shoulders and head - in particular, don't round your shoulders or lean forward. When doing triceps exercises, the chest should be open, the press should be tense. Otherwise, the load is transferred to the shoulder joints.
Read more
SAVE TO ...